Making Detrend¶
You need to prepare:
for making detrend. The analysis is carried out in order of making Bias, Dark, Flat and Fringe data. Note that Fringe data is usually required only for the analysis in Y-band. You can make these detrends by following instructions here.
Making Bias data¶
Bias data is made by removing an overscan from a 0 sec integration data (Bias raw data). Each CH of one HSC’s CCD has a 16 pixels overscan region at the left or right edge of the CH (see hscccd more detail). HSC pipeline evaluates the mean value to the short, fits spline to the longest axis of the overscan region, and subtract this value from Bias raw data. Finally bias data are produced after removing some outliers from these data. It will be done by HSC pipeline command of reduceBias.py.
# making Bias data
# home = ~
reduceBias.py $home/hsc --calib=$home/hsc/CALIB --rerun=calib_dith_16h_bias --id visit=902670..902678:2 --detrendId calibVersion=all
# Usage:
# reduceBias.py <a directory for data reduction> --calib=<a directory for detrend data> --rerun=<rerun name> --id visit=<visit ID of Bias raw data> --detrendId calibVersion=<version for making detrend>
#
# Parameters:
# --calib :A directory for detrend data
# --rerun :Rerun name
# --id :Specifying Bias raw data to make Bias data.
# In example, we specify visit IDs from 902670 to 902678 with 2 increment.
# (i.e. visit IDs 902670, 902672, 902674, 902676, and 902678)
# --detrendId:Specifying version for making detrend (option).
Warning
You must use the regular expression of [A-Za-z0-9_+-], when you set parameters of –calib and calibVersion. It means that ‘.’ and ‘,’ are not available.
You can use a batch process (this batch process means the one which the job is submitted to job control system) for all commands of making detrends in HSC pipeline. The pipeline provides batch process options depending on your machine environments. Note that the options are slightly different between pipeline versions.
Warning
HSC data analysis machine for open use(hanaco)does not have job control system. So please add the option in “Running a process in local machine”.
# Running a process in local machine (ex 4 threads)
# hscPipe ver 3.x
reduceBias.py --... --do-exec --mpiexec "-n 4"
# hscPipe ver 4.x
reduceBias.py --... --batch-type=smp --cores=4
# Submitting a batch script to another machine and running the script
# (ex 2 nodes 2 processes: 4 threads in total)
# hscPipe ver 3.x
reduceBias.py --... --nodes 2 --procs 2
# hscPipe ver 4.x
reduceBias.py --... --nodes 2 --cores 2
Once you perform reduceBias.py, you can find following data in your repository. Final Bias and intermediate data is produced in ~/hsc/CALIB and ~/hsc/rerun/[rerun], respectively.
- Bias data :BIAS-[ccd].fits in $home/hsc/CALIB/BIAS/[dateObs]/[filter]/[calibVersion]/
- A result of overscan subtraction for each [visit, ccd] Bias raw data:oss-[visit]-[ccd].png in $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun]/[pointing]/[filter]/thumbs/
- Bias data for each [visit, CCD] :c[ccd].fits in $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun]/postISRCCD/v[visit]-f[filter]/
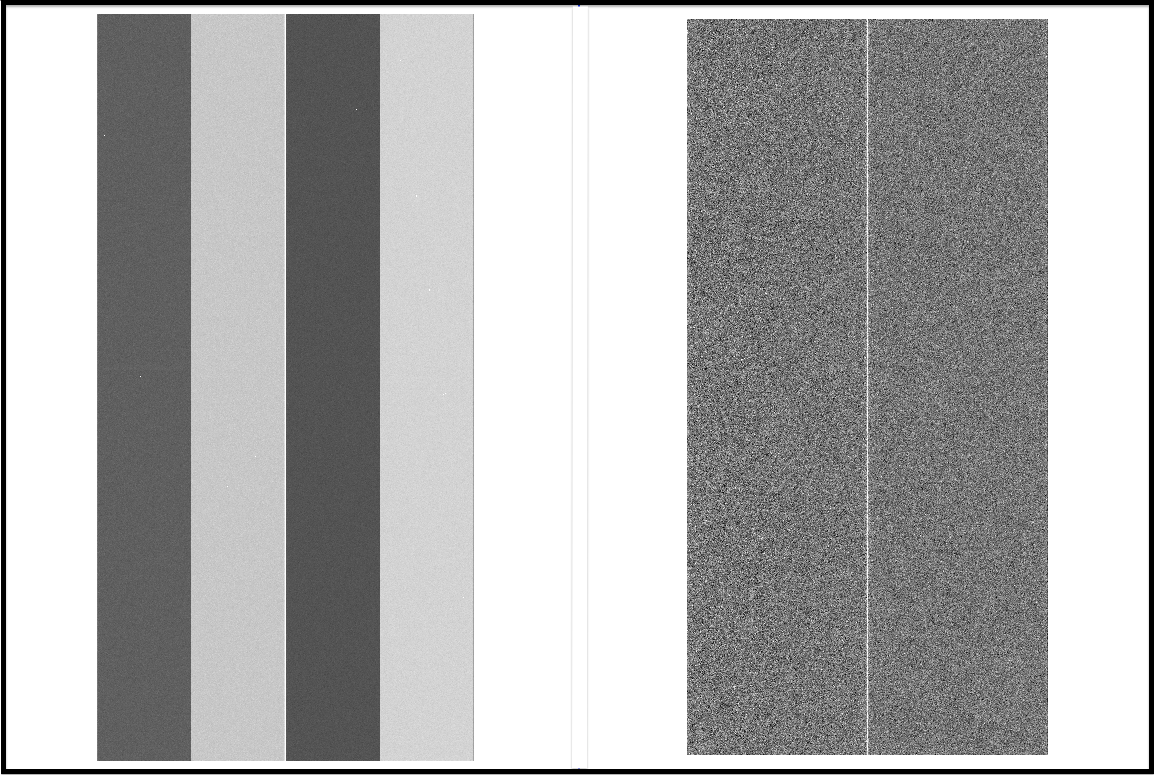
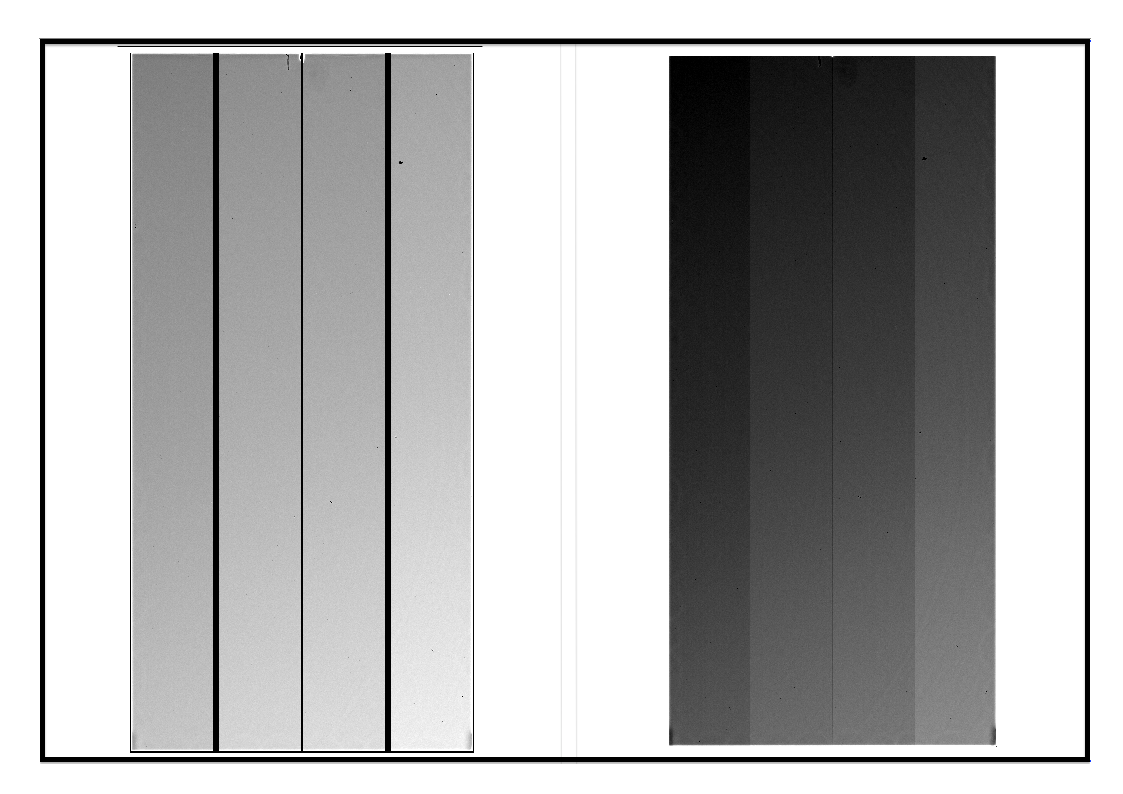
We shows Bias raw data (left) and Bias data produced by reduceBias.py (right) in Figure 1. Bias data is slightly smaller than Bias raw data, since overscan and prescan regions are left unattended in Bias data. You may also confirm a line in the direction of Y-axis around the center of Bias data. It is because that count values in these pixels are much higher than the rest of pixels which have nearly 0 values.
After you confirm your Bias data, you must register the data to a registry. Any following data reduction will be less successful without registering the data.
# Registering Bias data to calib-registry
genCalibRegistry.py --create --root=$home/hsc/CALIB --camera=HSC --validity=1000
# Usage:
# genCalibRegistry.py --create --root=<a directory for detrend data> --camera=HSC --validity=<days>
#
# Parameters:
# --create :A statement for creating new directory for detrend data
# --root :A directory for detrend data
# --camera :Instruction name. It definitely HSC
# --validity :Usable days of Bias data(default=12)
# The parameter means that this Bias data is available for the on-source data sandwiched XX days including the day of Bias observation.
# Since you may observe Bias and sources in very different day, you need to specify appropriate days for this parameter.
# In the example, we set validity=1000, because obs-date of Dark data is different more than a year from the one of Bias and Flat data.
Making Dark data¶
Dark data is used to correct dark current in a CCD stored within any integration time, and is made from Dark raw data by subtracting an overscan and Bias data. In HSC pipeline, the mean value of an overscan is subtracted from Dark raw data of each [visit, CCD]. And then, Bias data is subtracted from this overscan-subtracted Dark data. It is final Dark data. This process will be done by HSC pipeline command of reduceDark.py
# Making Dark data
reduceDark.py $home/hsc --calib=$home/hsc/CALIB --rerun=calib_dith_16h_dark --id visit=6600 --detrendId calibVersion=all
# Usage:
# reduceDark.py <a directory for data reduction> --calib=<a directory for detrend data> --rerun=<rerun name> --id visit=<visit ID of Dark raw data> --detrendId --detrendId calibVersion=<version for making detrend>
Note
General parameters of reduceDark.py are same as reduceBias.py.
Once reduceDark.py is done, you can find following data in your repository. Final Dark and intermediate data is produced in $home/hsc/CALIB and $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun], respectively
- Dark data :DARK-[ccd].fits in $home/hsc/CALIB/DARK/[dateObs]/[filter]/[calibVersion]/
- A result of overscan subtraction for each [visit, ccd] Dark raw data:oss-[visit]-[ccd].png in $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun]/[pointing]/[filter]/thumbs/
- A result of flattened by Flat data for each [visit, CCD] (※1) :flattened-[visit]-[ccd].png in $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun]/[pointing]/[filter]/thumbs/
- Dark data for each [visit, CCD] :c[ccd].fits in $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun]/postISRCCD/v[visit]-f[filter]/
Note
※1 Although Dark raw data does not flattened by Flat data during the process of reduceDark.py, flattened-[visit]-[ccd].png files are produced by default. If these files are unnecessary for you, they do not produced with –config doWriteFlattenedThumb=False parameter when you perform reduceDark.py.
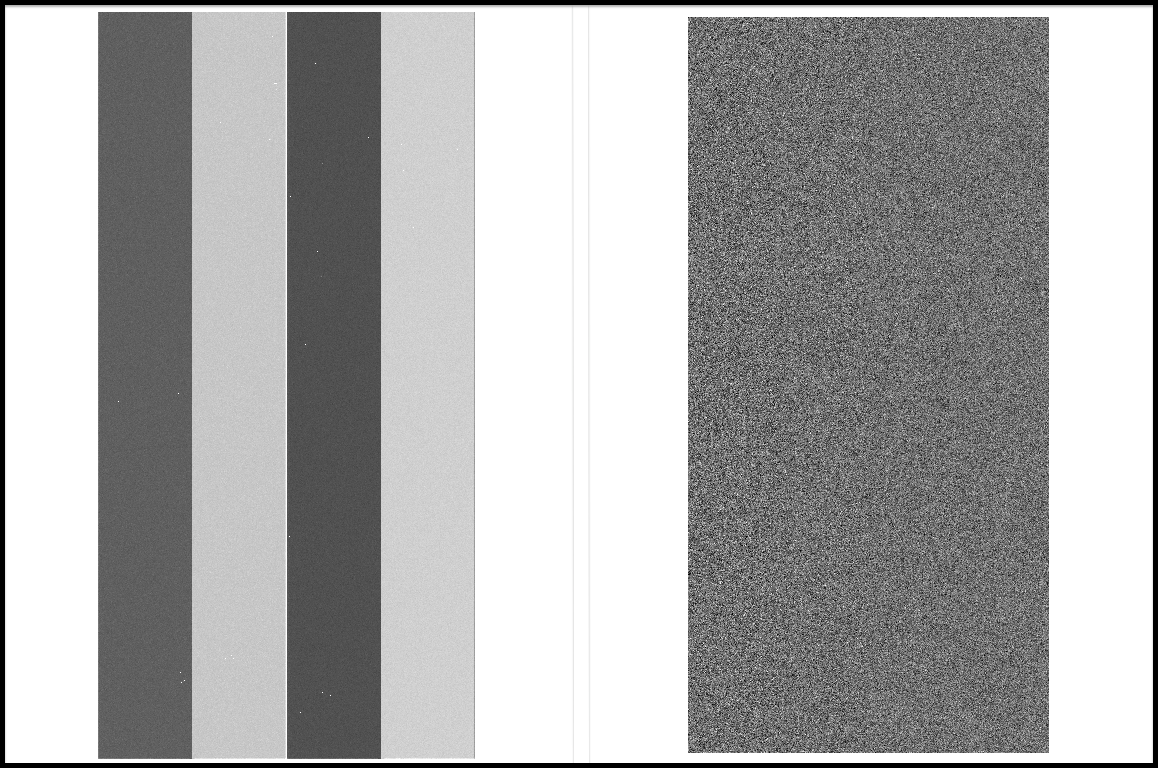
We present Dark raw data (left) and Dark data produced by reduceDark.py (right) in Figure 2. Dark data is slightly smaller than Dark raw data as is the case with Bias data, because overscan and prescan regions are removed from Dark raw data. Pixel values in Dark data are almost exactly zero.
After you confirm your Dark data, you must register the data to a registry
# Registering Dark data to calib-registry
genCalibRegistry.py --root=~/hsc/CALIB --camera=HSC --validity=1000
Note
You do not need add –create parameter when you perform genCalibRegistry.py, since you have already created a calib-registry when you register Bias data.
Making Flat data¶
There are two types of Flat data. One is dome Flat which is observed by illuminating a screen or wall. The other is night sky Flat which is made from on-source data. Here we introduce how to make dome Flat, because HSC observations mainly use it. If you want to make night sky Flat, please see the page of Making night sky Flat.
Flat data is made from dome Flat (Flat raw data) by removing an overscan, and subtracting Bias and Dark data. In HSC pipeline, at first, the mean value of an overscan is subtracted from Flat raw data of each [visit, CCD]. Then, we can obtain final Flat data by subtracting Bias and Dark data, respectively. It will be done by HSC pipeline command of reduceFlat.py.
# Making Flat data
reduceFlat.py $home/hsc --calib=$home/hsc/CALIB --rerun=calib_dith_16h_flat --id visit=902690..902704:2 --detrendId calibVersion=all
# Usage:
# reduceFlat.py <a directory for data reduction> --calib=<a directory for detrend data> --rerun=<rerun name> --id visit=<visit ID of Flat raw data> --detrendId --detrendId calibVersion=<version for making detrend>
Warning
You must make Flat data for each filter. For example, if you use i-band and r-band, you need to make i-band and r-band Flat data, respectively.
Once you perform reduceFlat.py you can find following data in your repository. Final Flat and intermediate data is produced in $home/hsc/CALIB and $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun], respectively.
- Flat data :FLAT-[ccd].fits in $home/hsc/CALIB/FLAT/[dateObs]/[filter]/[calibVersion]/
- A result of overscan subtraction for each [visit, ccd] Flat raw data:oss-[visit]-[ccd].png in $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun]/[pointing]/[filter]/thumbs/
- A result of flattened by Flat data for each [visit, CCD] :flattened-[visit]-[ccd].png in $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun]/[pointing]/[filter]/thumbs/
- Flat data for each [visit, CCD] :c[ccd].fits in $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun]/postISRCCD/v[visit]-f[filter]/
Flat raw data (left) and Flat data produced by reduceFlat.py (right) are shown in Figure 3. Flat data is slightly smaller than Flat raw data as is the case with Bias and Dark data, because overscan and prescan regions are removed from Flat raw data.
After you confirm your Flat data, you must register the data to a registry
# Registering Flat data to calib-registry
genCalibRegistry.py --root=$home/hsc/CALIB --camera=HSC --validity=1000
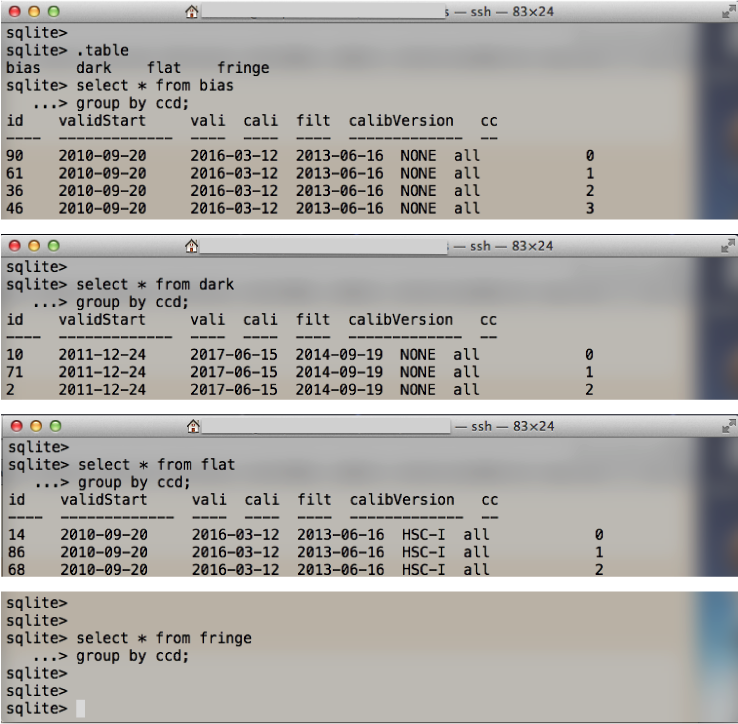
Now we prepare all detrend data. Let’s check a calib-registry whether we do not forget to register of detrend data.
sqlite> .table # display the table contents
bias dark flat fringe
sqlite> select * from bias # select header information of Bias data
...> group by ccd; # display in order of ccd
# search results
#
id validStart vali cali filt calibVersion cc
---- ------------- ---- ---- ---- ------------- --
90 2010-09-20 2016-03-12 2013-06-16 NONE all 0
61 2010-09-20 2016-03-12 2013-06-16 NONE all 1
...
It is ok to confirm that all detrend data of Bias, Dark, and Flat data is registered in a calib-registry (see Figure 4). Note that if you type select * from fringe, you can get no response. Because we do not make Fringe data.
Making Fringe data¶
Fringe is the pattern caused by interference between surface of CCD and it becomes obviously in longer wavelength. HSC pipeline can support Y-band and NB0921. Fringe data is made from stacked object data. And then, it is subtracted from object data assuming the pattern is constant and its intensity is proportional to the integration. It will be done by HSC pipeline command of reduceFringe.py.
# Making Fringe data
reduceFringe.py $home/hsc --calib=$home/hsc/CALIB --rerun=calib_fringe --id visit=6772..6782:2 --detrendId calibVersion=all
# Usage:
# reduceFringe.py <a directory for data reduction> --calib=<a directory for detrend data> --rerun=<rerun name> --id visit=<visit ID of object data> --detrendId --detrendId calibVersion=<version for making detrend>
Once you perform reduceFringe.py you can find following data in your repository. Final Fringe and intermediate data is produced in $home/hsc/CALIB and $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun], respectively.
- Fringe data :FRINGE-[ccd].fits in $home/hsc/CALIB/FRINGE/[dateObs]/[filter]/[calibVersion]/
- A result of overscan subtraction for each [visit, ccd] Fringe raw data:oss-[visit]-[ccd].png in $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun]/[pointing]/[filter]/thumbs/
- A result of flattened by Flat data for each [visit, CCD] :flattened-[visit]-[ccd].png in $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun]/[pointing]/[filter]/thumbs/
- Fringe data for each [visit, CCD] :c[ccd].fits in $home/hsc/rerun/[rerun]/postISRCCD/v[visit]-f[filter]/
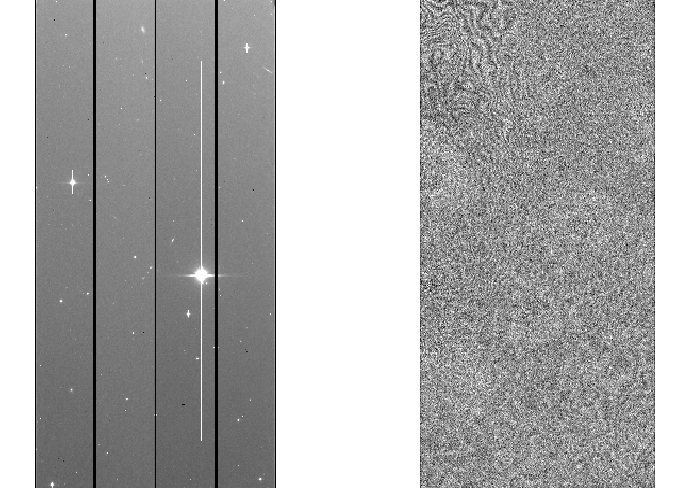
Fringe raw data (left) and Fringe data produced by reduceFringe.py (right) are shown in Figure 5. Fringe data is slightly smaller than Fringe raw data, because overscan and prescan regions are removed from Fringe raw data.
After you confirm your Fringe data, you must register the data to a registry
# Registoring Fringe data
genCalibRegistry.py --root=$home/hsc/CALIB --camera=HSC