Description of global sky subtraction¶
hscPipe 6 or later generates SKY image to correct the over sky subtraction around bright objects (global sky subtraction). SKY image is a background model, the response of camera to the sky. This procedure is related with ConstructSky.py, skyCorrection.py and coaddDriver.py. Fig. 1 shows the processes of global sky subtraction.
Just after coadd (deepCoadd/[filter]/[tract]/[patch].fits), large scale pattern is subtracted but local sky remains. The local sky subtraction is performed when hscpipe detects objects (deepCoadd-results/[filter]/[tract]/[patch]/calexp*.fits). Catalog is generated based on calexp*.fits.
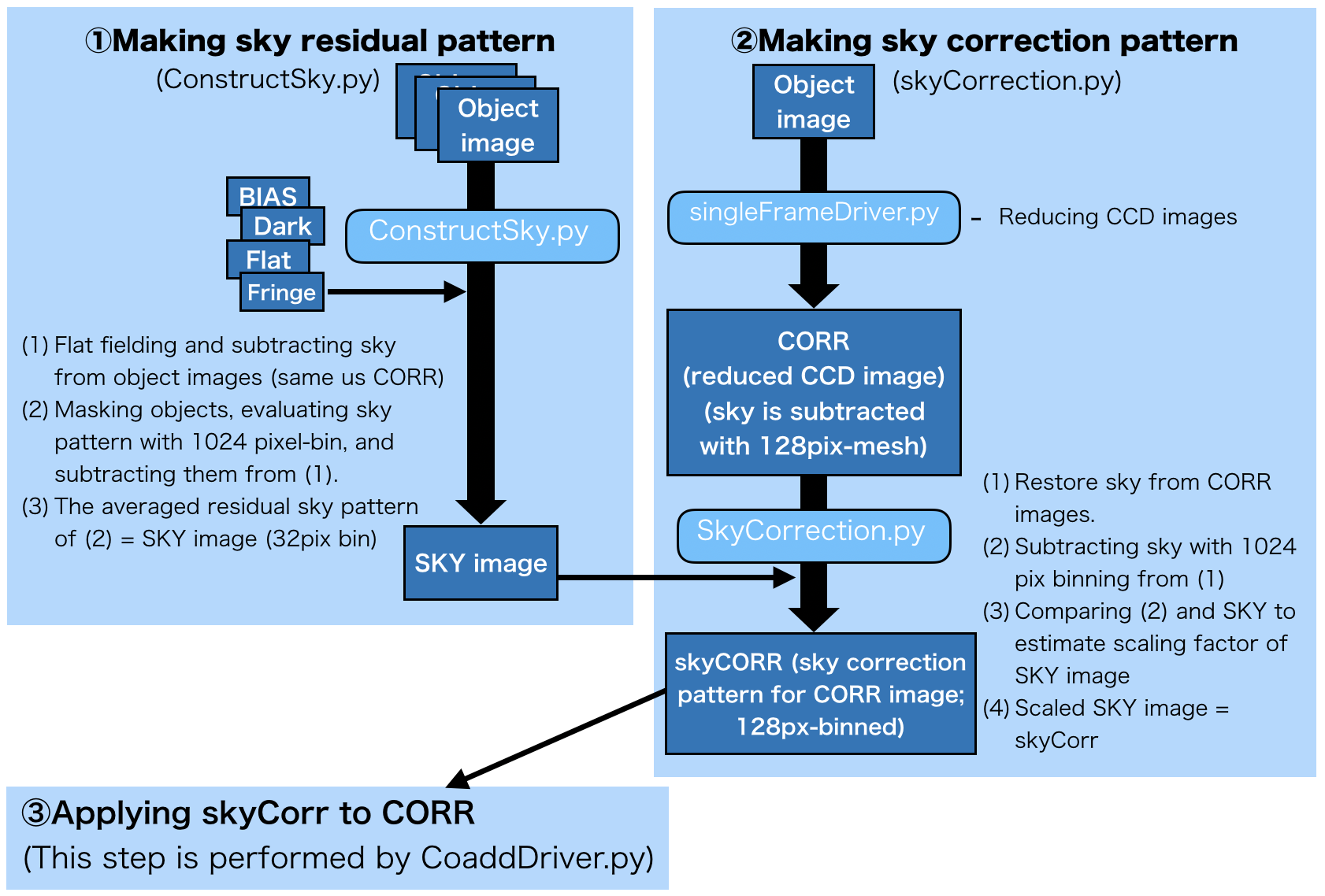
Figure 1. Process of global sky subtraction¶
1. Making sky pattern¶
First of all, you generate SKY image with ConstructSky.py. In this step, you use BIAS, Dark, Flat, Fringe images and object raw images. ConstructSky.py should be done per filter. After performing flat fielding and sky subtraction on object ccd images, masking objects and subtracting large scale sky pattern by 1024 pixel bin which originates in e.g., moon light and differs by shot. The stacked images of them is SKY image. Ideally, use >50 shots (at least >20 shots) to make SKY images.
2. Scaling sky correction pattern for CORR¶
After SingleFrameDriver.py, makeDiscreteSkyMap.py and mosaic.py (we note that mosaic.py can be run in parallel with skyCorrection.py), you generate sky correction pattern for reduced CCD images (CORR). In default, SKY is subtracted with 128 pixel bin.
3. Correct sky pattern¶
In this step, the processing determined a reference band (ref-[tract]-[patch].fits) from meas catalogs in each filter. In this process, the contents of meas catalogs of reference filter for each objects are gathered and summarized. Then the reference band is defined from the result of meas considering the same priority in merge process.
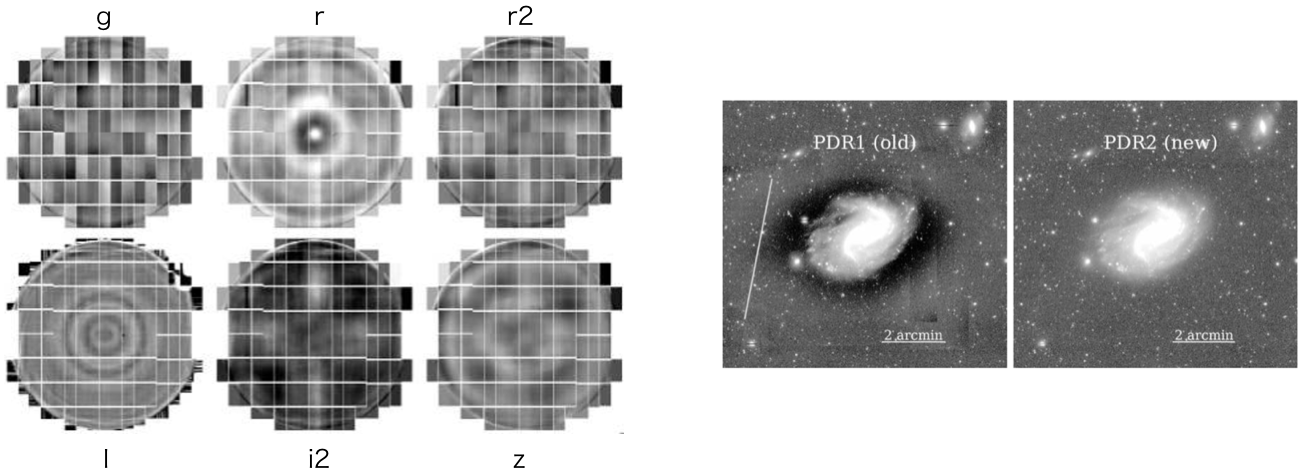
Figure 1. Performance of global sky subtraction (from HSC-SSP pdr2 paper).¶
